Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy in Edmonton. Pelvic floor physical therapy […]
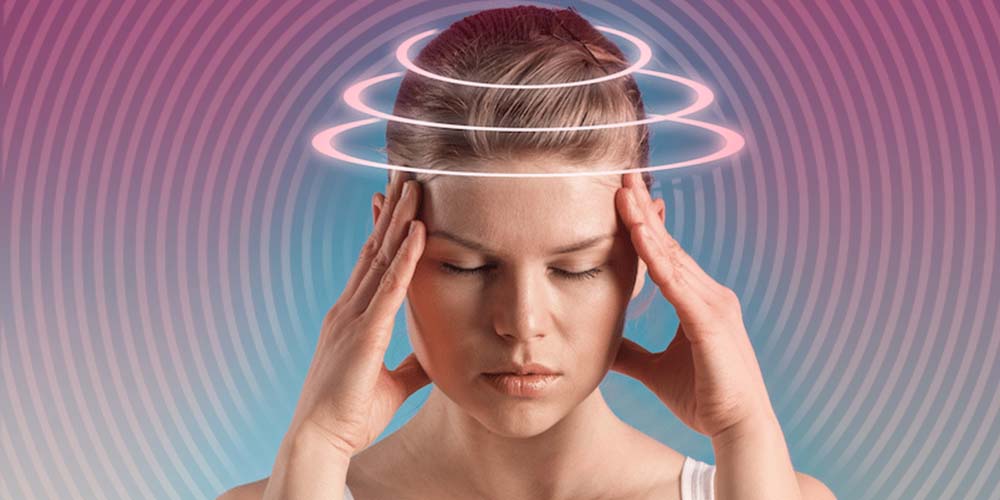
What is Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy? How It Works.
What is Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy:
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is a specialized form of physical therapy designed to address vestibular disorders, which affect the inner ear and vestibular system responsible for balance and spatial orientation. VRT aims to alleviate symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, imbalance, and visual disturbances by promoting central nervous system compensation and adaptation. Here’s how vestibular rehabilitation therapy works:
1. Assessment and Diagnosis:
- The first step in vestibular rehabilitation therapy is a comprehensive assessment conducted by a qualified healthcare professional, typically a physical therapist specializing in vestibular disorders.
- During the assessment, the therapist evaluates the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and functional limitations, as well as performs a series of tests to assess balance, gait, coordination, and vestibular function.
2. Individualized Treatment Plan:
- Based on the assessment findings, the physical therapist develops an individualized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs and goals.
- The treatment plan may include a combination of exercises, maneuvers, and strategies aimed at improving balance, reducing dizziness, and enhancing functional abilities.
3. Habituation Exercises:
- Habituation exercises are a core component of vestibular rehabilitation therapy, particularly for patients experiencing symptoms of dizziness or vertigo triggered by head movements or changes in position.
- These exercises involve repetitive exposure to movements or positions that provoke symptoms, with the goal of desensitizing the vestibular system and reducing the intensity and frequency of symptoms over time.
4. Gaze Stabilization Exercises:
- Gaze stabilization exercises focus on improving visual stability and reducing visual disturbances associated with vestibular dysfunction, such as oscillopsia (blurred vision with head movements).
- These exercises typically involve tracking moving objects or performing head movements while maintaining focus on a stationary target, helping to enhance the coordination between eye movements and head movements.
5. Balance Training:
- Balance training exercises aim to improve static and dynamic balance, proprioception (awareness of body position in space), and postural control.
- These exercises may include standing on various surfaces, performing weight shifts, practicing tandem walking, and challenging balance reactions in different positions to enhance stability and confidence during daily activities.
6. Canalith Repositioning Maneuvers:
- For patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), a common vestibular disorder characterized by brief episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements, canalith repositioning maneuvers may be performed.
- These maneuvers, such as the Epley maneuver or Semont maneuver, aim to reposition displaced calcium carbonate crystals (canaliths) within the inner ear’s semicircular canals, relieving symptoms of vertigo associated with BPPV.
7. Education and Lifestyle Modifications:
- Throughout vestibular rehabilitation therapy, patients receive education about their condition, triggers for symptoms, and strategies for managing symptoms in daily life.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding sudden head movements, maintaining hydration and adequate rest, and minimizing stress, may also be recommended to optimize treatment outcomes and prevent symptom exacerbation.
8. Progress Monitoring and Adjustment:
- Vestibular rehabilitation therapy is typically conducted over a series of sessions, during which the patient’s progress is monitored closely, and the treatment plan may be adjusted accordingly based on response to interventions.
- Regular reassessment allows the therapist to track improvements, address any challenges or setbacks, and ensure that the patient is progressing toward their functional goals effectively.
In summary, vestibular rehabilitation therapy is a structured and evidence-based approach to addressing vestibular disorders and associated symptoms. By targeting specific impairments and promoting adaptation and compensation within the vestibular system, VRT helps patients regain balance, reduce dizziness, and improve overall quality of life. If you’re experiencing symptoms of vestibular dysfunction, consider consulting a qualified healthcare professional by calling at 780-440-9003, such as a physical therapist specializing in vestibular rehabilitation, to explore the benefits of VRT for your condition.